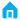
Indoor Luminaire Distribution Classification (CIE Standard)
| Type |
Up/Down Light Ratio |
Application Scenarios |
Design Considerations |
| Direct |
≥90% Down |
Offices, Classrooms, Main Store Lighting |
Requires glare control (UGR < 19), and pairing with a cutoff angle ≥30∘ (presumably
referring to the beam angle for minimizing direct glare, though "cutoff angle" is a
specific term in lighting design related to shielding the light source to prevent
high-angle glare). |
| Semi-direct |
60−90% Down |
Conference Rooms, Corridors |
Avoid ceiling brightness, upward light ratio ≥10% |
| Direct-Indirect |
50% Up and Down |
Hotel Lobbies, Libraries |
Luminaire mounting height $geq2.8$m, ensuring up/down light balance |
| Indirect |
≥90% Up |
High-end Offices, Exhibition Halls |
Ceiling reflectance ≥80%, can be highly efficient |
| Diffuse |
Balanced Up/Down Light |
Restaurants, Home Spaces |
Suitable for high-transmittance materials (e.g., milky white acrylic/frosted glass) |

IES and NEMA Outdoor Lighting Classification
IES Five Types of Light Distribution (for Street and Area Lighting)
IES classifies luminaires into five types (Type I through Type V) of light distribution patterns based on illuminance distribution in the roadway direction for different scenarios such as streets, plazas, sidewalks, parking lots, and more. Each type of luminaire has a specific light intensity distribution pattern for optimizing lighting efficiency and uniformity.
| Type |
Light Distribution Pattern |
Typical Application |
| Type I |
Narrow Asymmetric |
Single-lane sidewalks, two-sided lighting, mounting width close to mounting height |
| Type II |
Medium Asymmetric |
Narrow streets, sidewalks, one-sided lighting for centerline illumination |
| Type III |
Mid-wide Asymmetric |
Urban branch roads, small squares, pole distance from roadside is relatively far |
| Type IV |
Forward Throw Asymmetric |
Parking lots, building facades, light intensity mainly concentrated directly forward |
| Type V |
Symmetrical Circular |
Central squares, open areas, mostly for central mounted luminaires |
| Type VS |
Symmetrical Square |
Crossroads, rectangular squares, light distribution is approximately square |

BUG Ratings (Backlight, Uplight, Glare)
| Module |
Meaning |
Corresponding Control Objective |
Application Significance |
| B - Backlight |
Backlight |
Prevent light spill into residential and non-target areas |
Reduce neighborhood interference |
| U - Uplight |
Uplight |
Reduce skyglow, star obscuration |
Mitigate light pollution |
| G - Glare |
High-angle glare |
Control intense stimulation to eyes or vehicle driving |
Enhance visual safety |

Grades from 0 (strictest) to 5 (most lenient) with subdivided Solid Angle for each dimension: e.g. BL-Low, UL-High, FH-High etc.

The BUG rating system is a crucial tool for lighting designers to select appropriate fixtures that minimize light pollution, conserve energy, and comply with "dark-sky" ordinances.
Main Luminaire Lighting Application Areas:
Indoor Lighting
Residential Lighting: Living rooms, bedrooms, kitchens, bathrooms, studies, etc., focusing on comfort, warm ambiance, and functionality (e.g., reading, cooking).
Office Lighting: Offices, conference rooms, corridors, etc., emphasizing high illuminance, uniformity, and low glare (UGR<19) to enhance work efficiency and comfort.
Commercial Lighting: Stores, shopping malls, restaurants, hotels, etc., focusing on product display, attracting customers, creating brand ambiance, and enhancing customer experience.
Industrial Lighting: Factories, warehouses, workshops, etc., emphasizing high brightness, durability, dustproof and waterproof features, safety, and reliability to meet specific production needs.
Educational Lighting: Classrooms, libraries, laboratories, etc., requiring sufficient and uniform brightness with no glare to protect students' eyesight.
Healthcare Lighting: Hospitals, operating rooms, clinics, etc., with extremely high requirements for color rendering, illuminance, uniformity, and shadow control to ensure precision in medical procedures.
Museum/Gallery Lighting: Emphasizing protection of exhibits (UV/IR filtering), color rendering, accent lighting, and ambiance creation.
Outdoor Lighting
Roadway Lighting: Streets, highways, tunnels, etc., ensuring night-time driving and pedestrian safety, and reducing traffic accidents. (This is where IES distribution types are applied).
Landscape Lighting: Parks, plazas, sculptures, building facades, etc., using light to highlight features, create nightscapes, and enhance urban aesthetics.
Sports Venue Lighting: Football fields, basketball courts, tennis courts, etc., meeting high requirements for brightness, uniformity, and glare control for athletes, spectators, and TV broadcasts.
Parking Lot Lighting: Providing ample brightness to ensure vehicle and pedestrian safety and improve visibility.
Security/Safety Lighting: Building perimeters, fences, entrances, etc., using lighting to deter crime and improve surveillance effectiveness.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!